Wind power in North Dakota today:
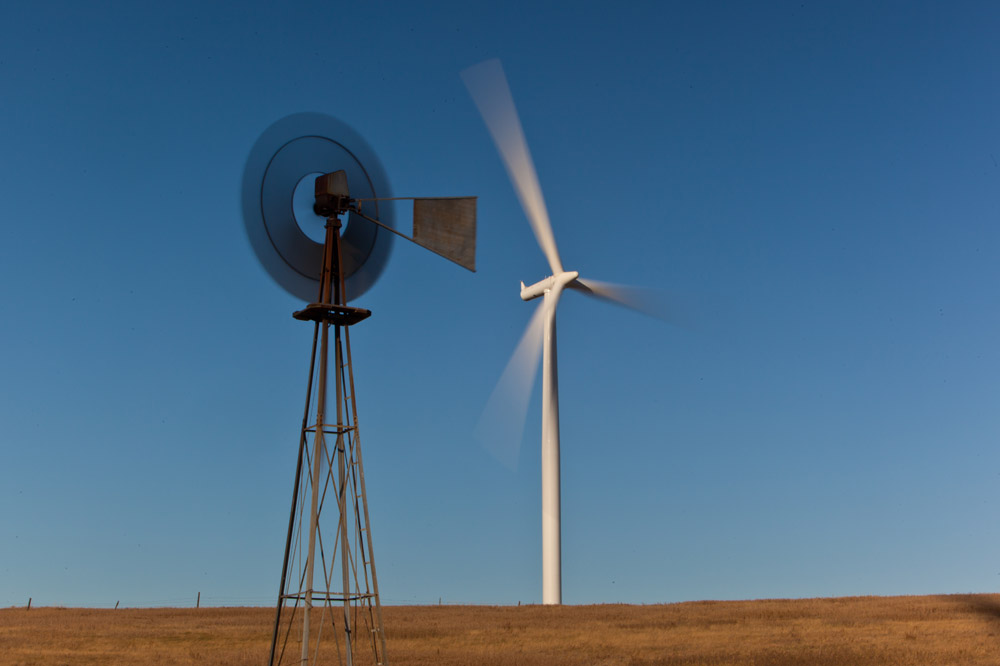
- Before modern power grids, small wind generators would produce power for individual homes and farms (see image 1). In recent years, wind power is again being used to generate electricity in North Dakota.
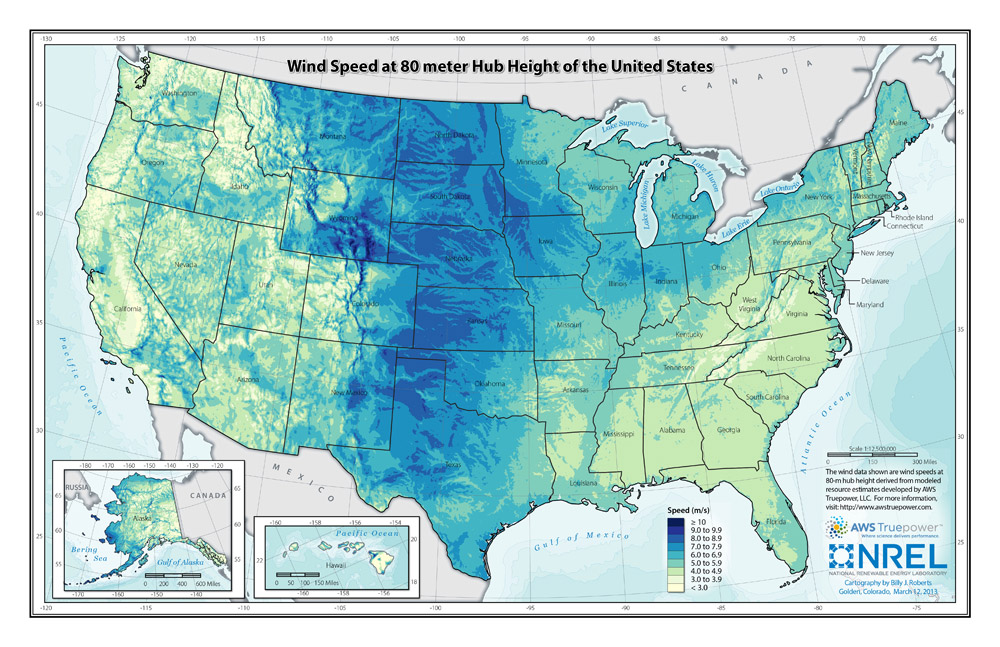
- North Dakota has a strong and endless supply of wind. But the wind is also intermittent, which means that it doesn't always blow. (See Image 2)
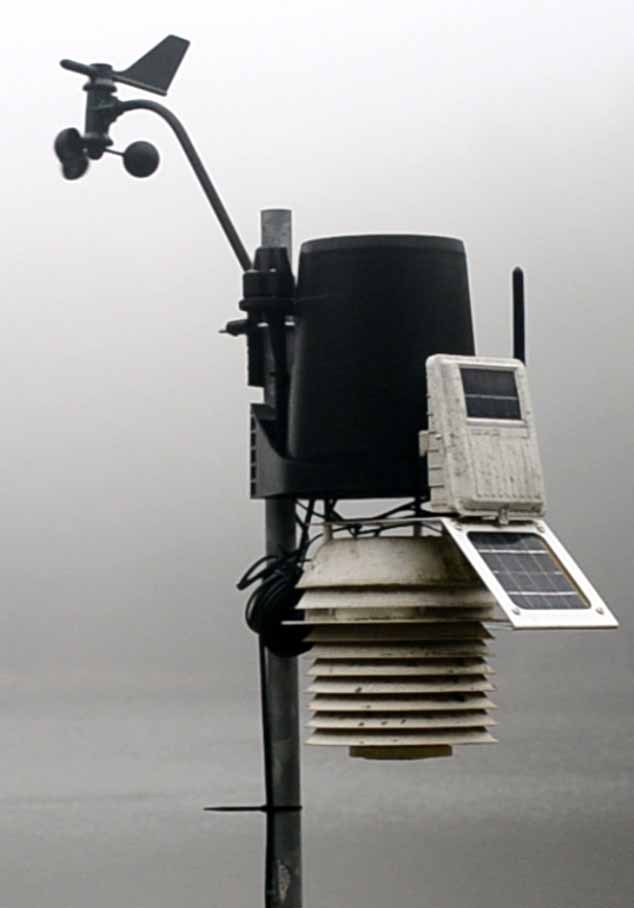

Anemometer — An anemometer (an-ah-MOM-ah-ter) is an instrument used to measure wind speed.
- Modern technology has made wind a more practical method of producing electricity.
- Giant wind turbines generate more than 20 percent (2017) of the state's electricity.
- More than 1,500 (2017) wind turbines are located in North Dakota.
- North Dakota ranks 11th in the country for the number of wind turbines in the state. Visit the U.S. Geological Survey to see where the wind farms are located in North Dakota.
- More than 1,500 (2017) wind turbines are located in North Dakota.
- Giant wind turbines generate more than 20 percent (2017) of the state's electricity.
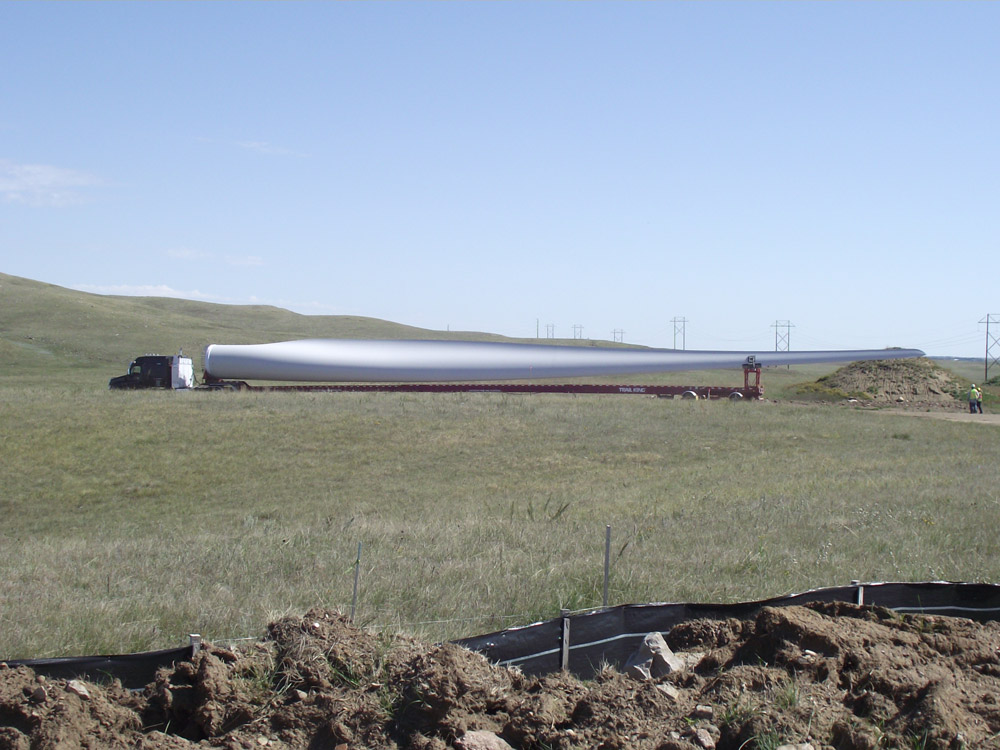
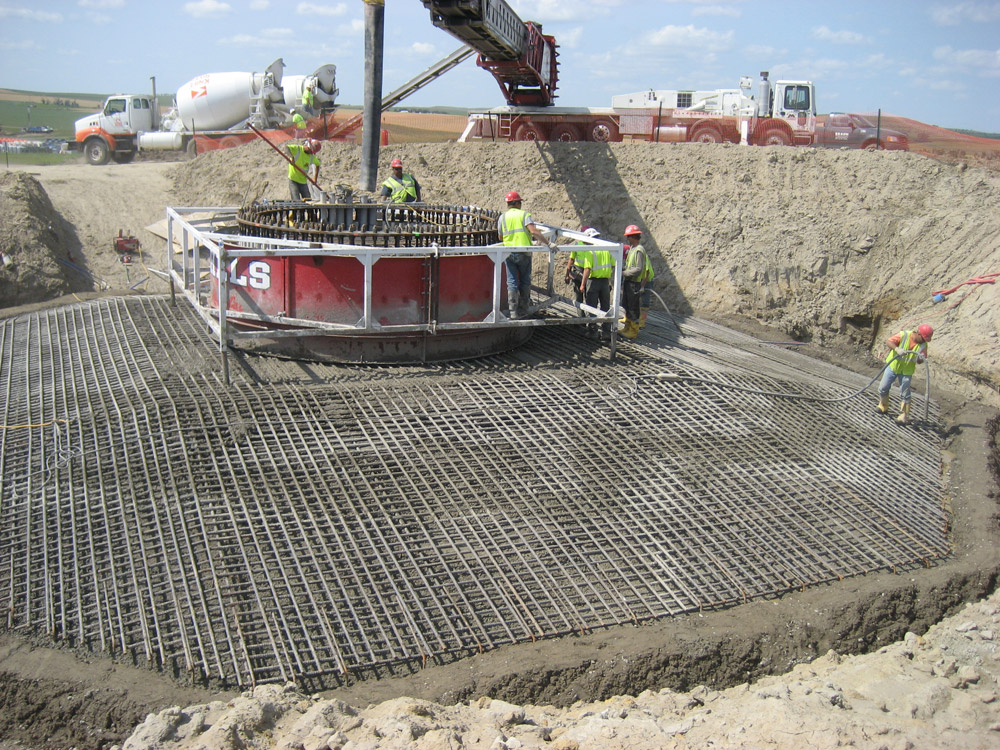
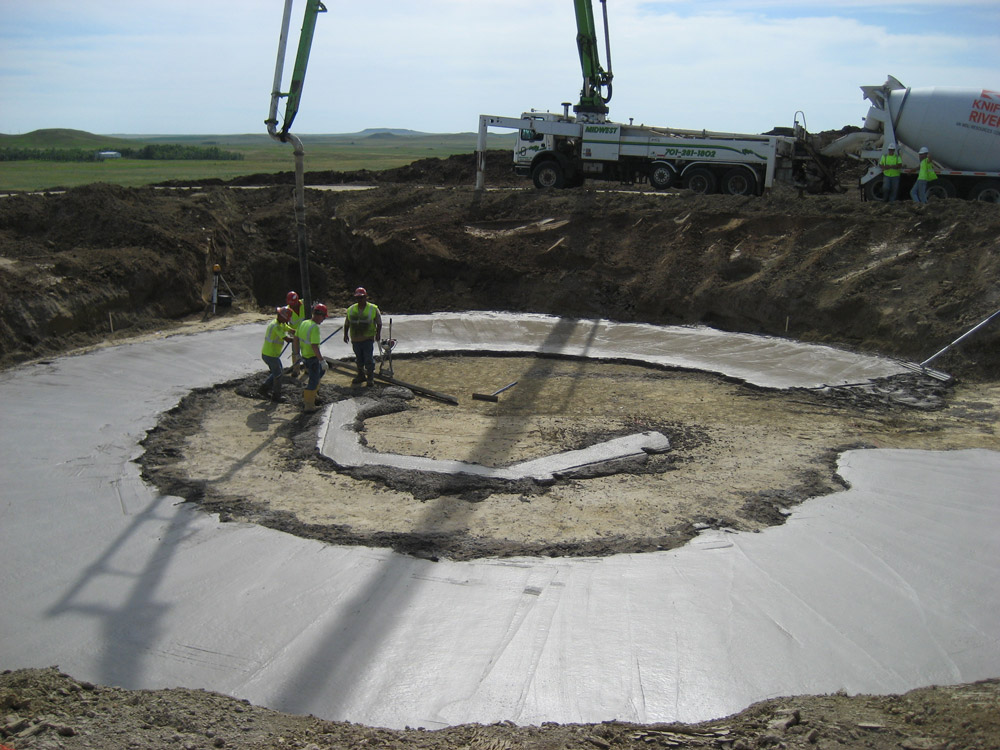
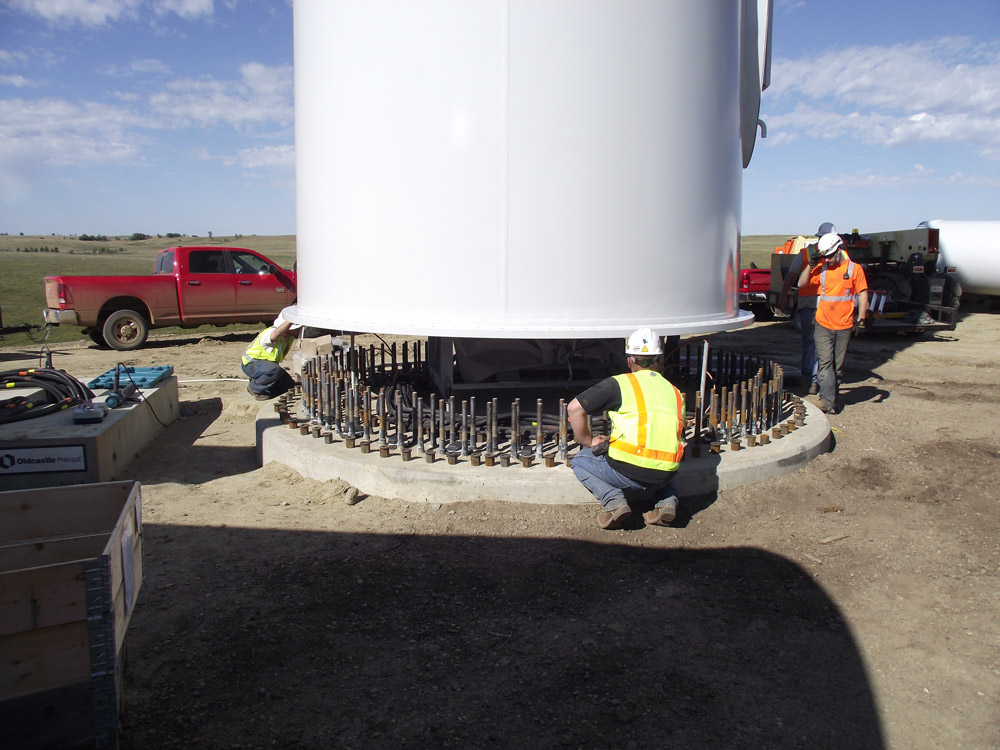
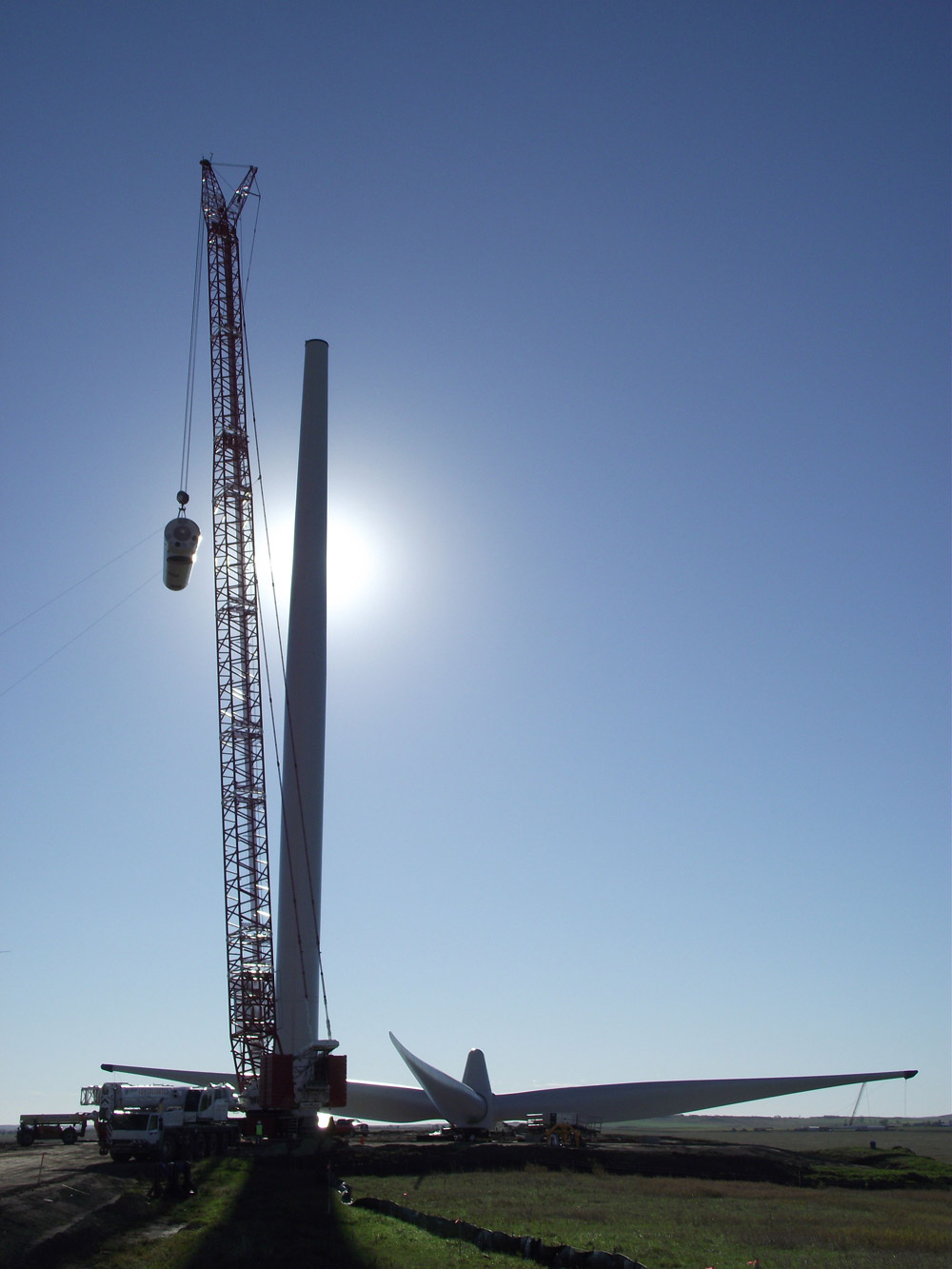
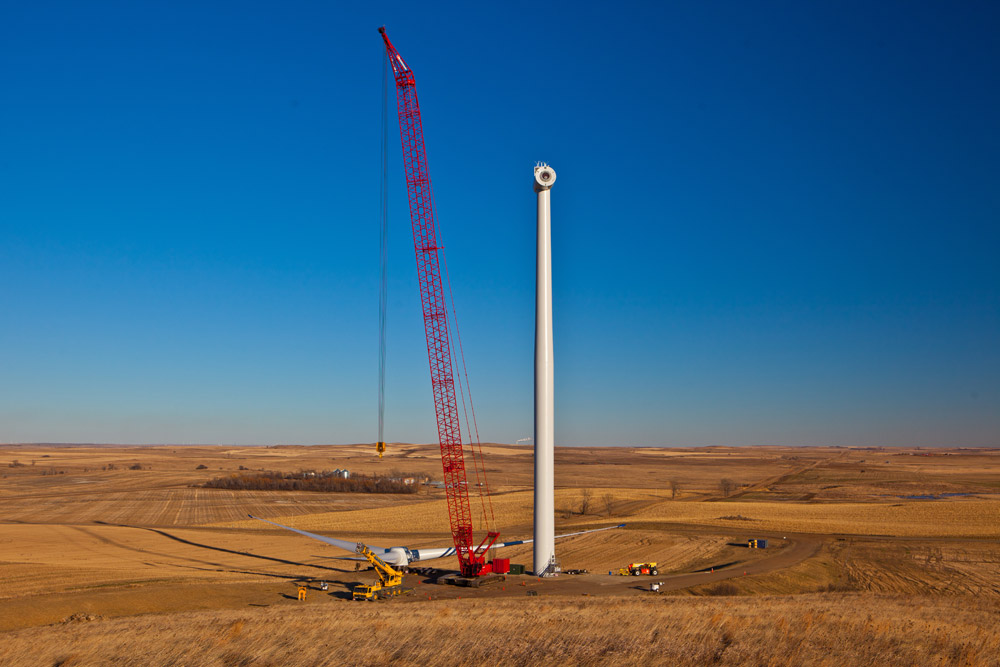
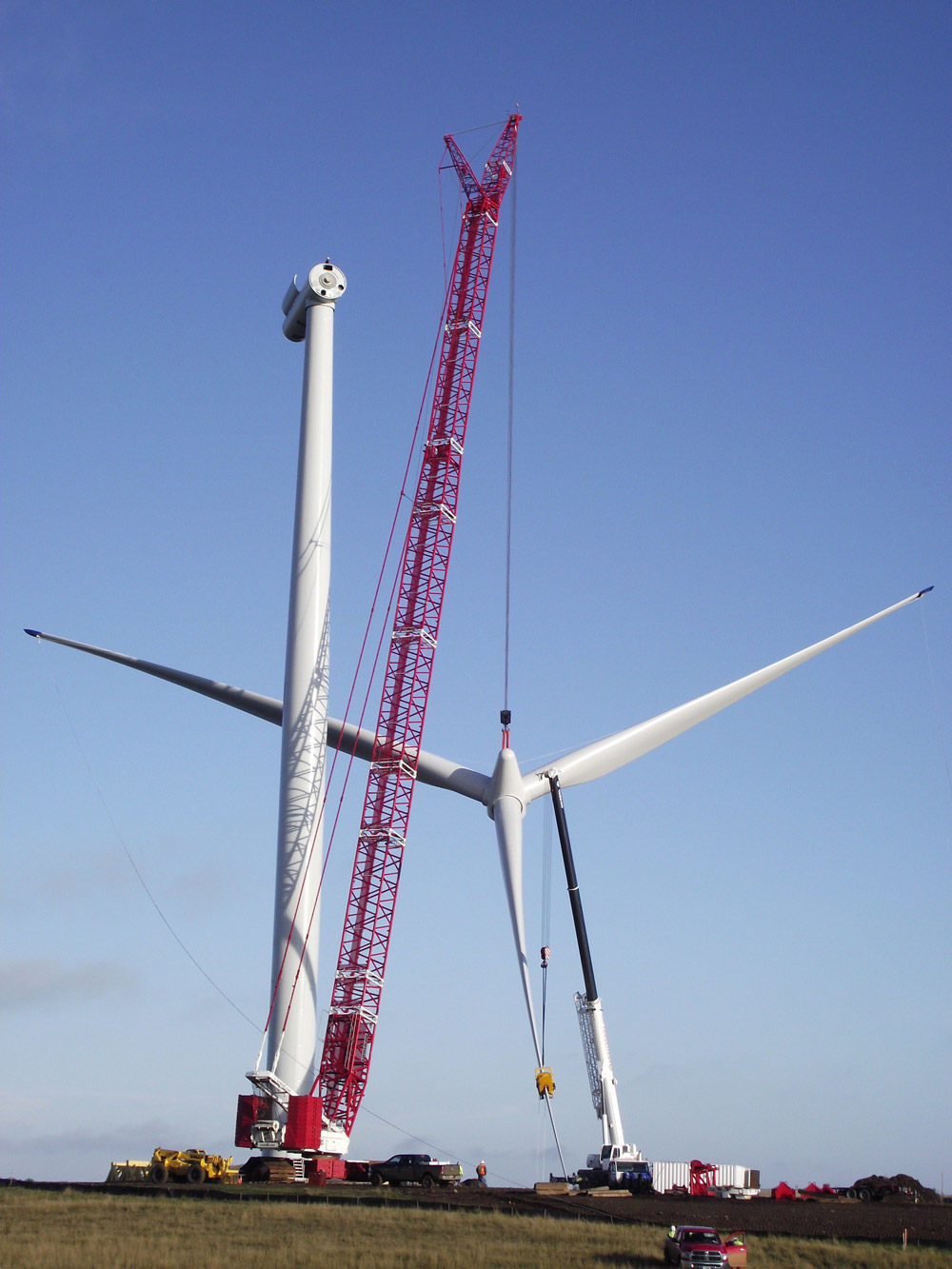
Construction of a Wind Turbine: See construction of a wind turbine at Basin Electric Power Cooperative's Wilton Wind Farm. Video courtesy of Basin Electric Power Cooperative.
How a turbine converts wind to electricity:
- A wind turbine has blades that spin when pushed by the wind. The blades are connected to a low-speed drive-shaft.
- The low-speed drive-shaft turns when the blades spin.
- The low-speed drive-shaft is connected to a gear box.
- Gears in the gearbox cause another drive-shaft to turn at a high rate of speed.
- The high-speed drive shaft is connected to an electrical generator.
- The drive shaft turns at a high speed inside the generator to produce electricity.
- Wires going down inside the turbine tower carry the electricity to a transmission line.
- A group of wind turbines is called a wind farm
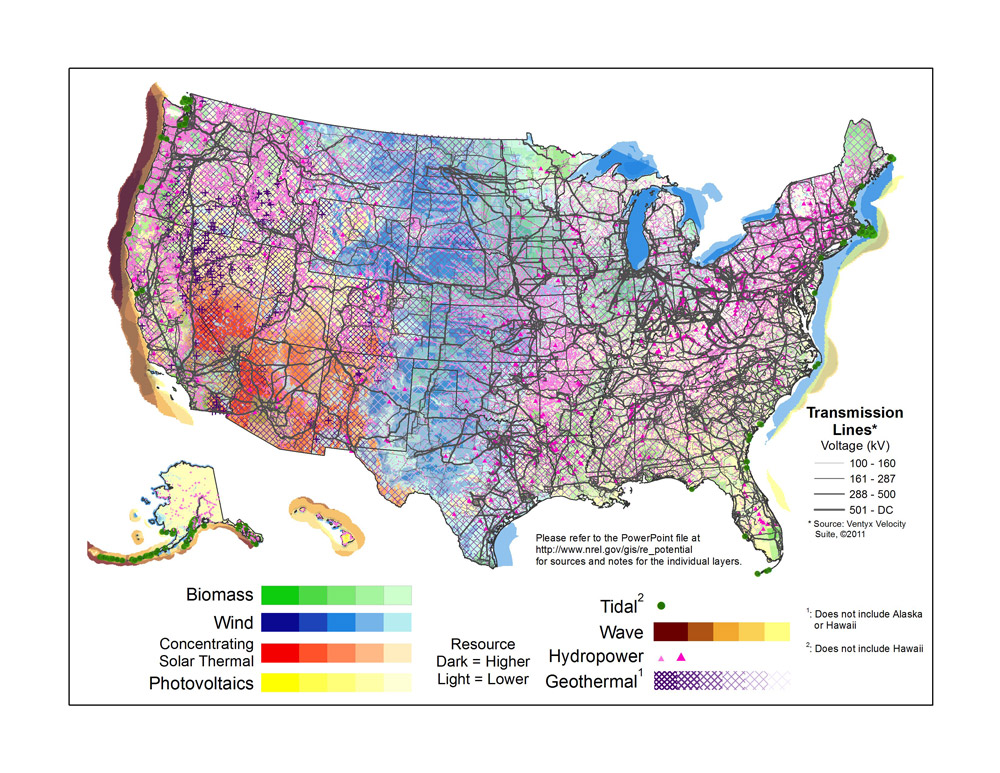
US Transmission Grid: This map shows renewable energy potential along with high voltage transmission lines throughout the United States – from 100 kilovolts and up. The smaller distribution lines (wires the carry electricity to homes) are not shown on this map. This map was created by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory for the US Department of Energy.
News Story on Turbine Construction: How Basin Electric builds a wind turbine. Video courtesy of Basic Electric Power Cooperative.
- North Dakota ranks third among the states for the percentage of electricity generated from wind power.
- Electricity from wind farms is carried by transmission lines to the electricity grid. Reference to "BSC Energy Flow" Tool
- The electricity grid is a network of connected power lines that carry electricity throughout the United States.