What geothermal energy is:
- Geothermal energyGeo = earth therm = heat. is heat from within the earth.
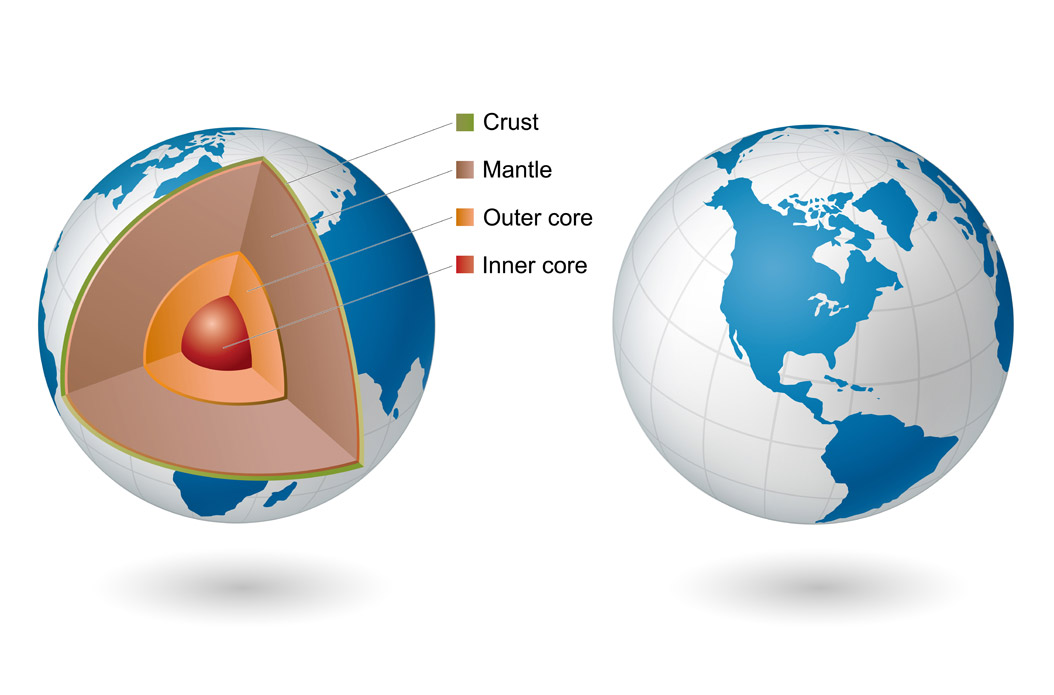
The Interior of the Earth
Interior of the Earth
- Diagram:
- Core:
- Almost 4,000 miles beneath the surface of the earth.
- Made of two layers: a solid iron core and an outer core made of magma (molten rock).
- Mantle:
- Surrounds the core.
- Is about 1,800 miles thick.
- Made of magma and rock.
- Crust:
- Outermost layer; forms continents and ocean floors.
- Can be 15 to 35 miles thick on land and 3 to 5 miles thick under oceans.
- Heat is always being created in the core of the earth from the slow, natural decay of radioactive particles.
- The temperature of the solid inner core is as hot as the surface of the sun – about 6,000° C, or 10,800° F.
- Rocks and water deep underground absorb this heat.
- The crust of the earth is broken into pieces called tectonic plates.
- Magma comes close the earth's surface near the edges of the plates.
- Rocks and water deep underground absorb heat from the magma.
- When magma comes close to the surface, it heats groundwater trapped in porous rock or in underground reservoirs.
- This heat can be recovered and used to heat buildings or generate electricity.
- Geothermal energy is renewable because heat is continuously being produced inside the earth.
- Magma comes close the earth's surface near the edges of the plates.
- The temperature of the solid inner core is as hot as the surface of the sun – about 6,000° C, or 10,800° F.
- Enhanced Geothermal Systems, or EGS, is a technology that produces electricity from the heat of the earth.
- EGS can be developed where the underground rock has a temperature higher than 150° C (300° F). Visit the Bismarck State College Animation Tool to see how geothermal energy works.
The process of Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS)
- Hot rock is fractured;
- Water is circulated through an underground system;
- Steam is created;
- The steam drives a turbine to generate electricity;
- The water is run back through the rocks to pick up more heat;
- The closed-loop cycle begins again.